Sunflower
General Description :
Height: Typically 5–12 feet (1.5–3.5 meters), but some varieties can grow taller.
Scientific name: Helianthus annuus
Family: Asteraceae (daisy family)
Native to: North America
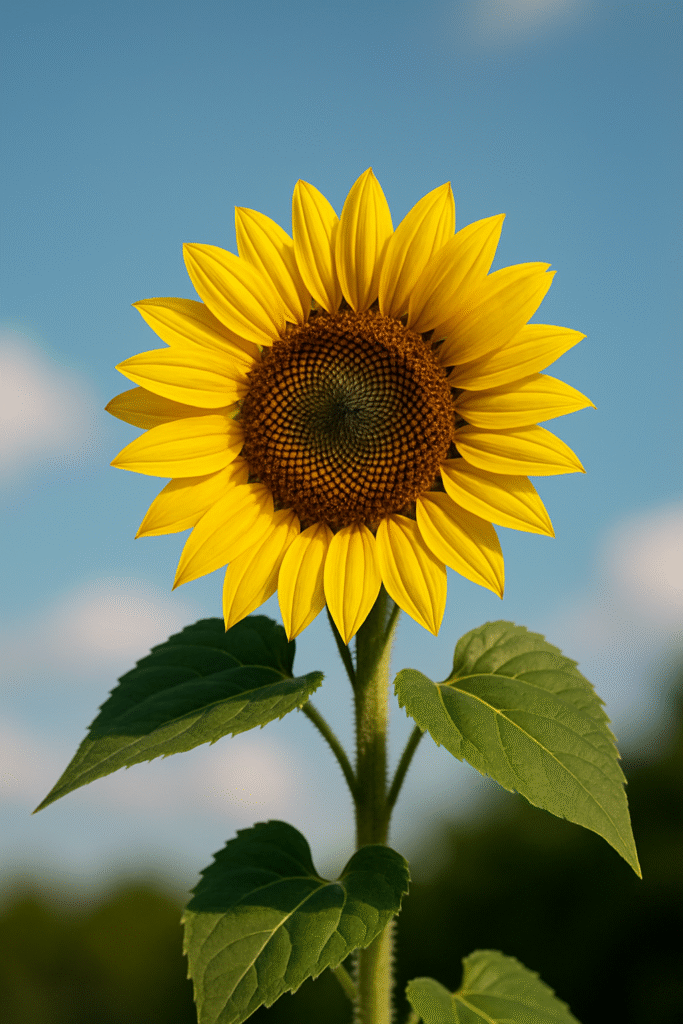


Distinct Features :
- Flower head: Composed of hundreds of tiny flowers (florets). The outer yellow petals are ray florets, and the center contains disc florets that mature into seeds.
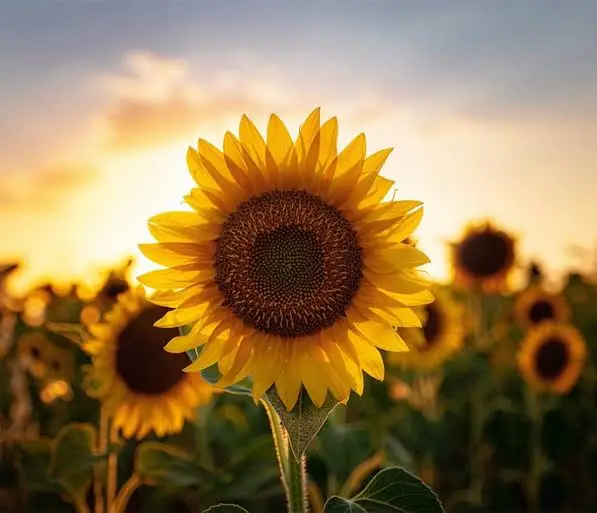
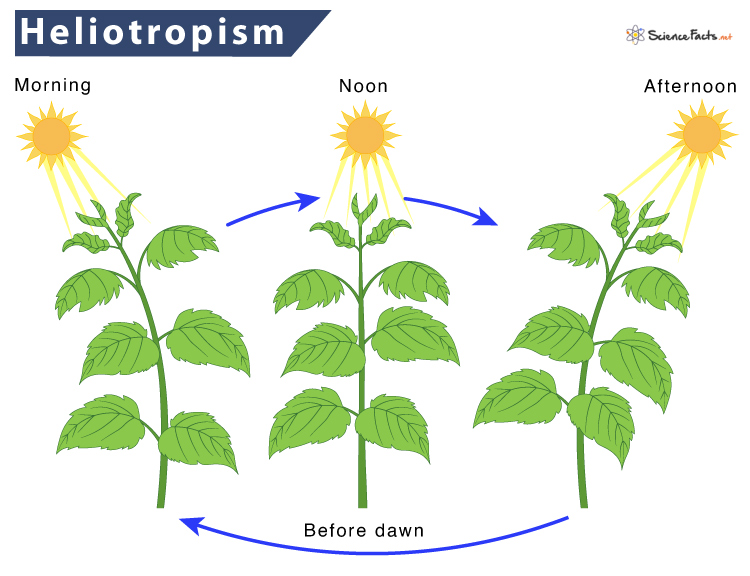

- Heliotropism
- Heliotropism: Young sunflowers track the sun’s movement across the sky, a phenomenon called heliotropism. Mature flowers usually reorient themselves during the night to face east in anticipation of the sunrise. Heliotropism optimizes light interception of young sunflower plants, increasing it by 10% or more.
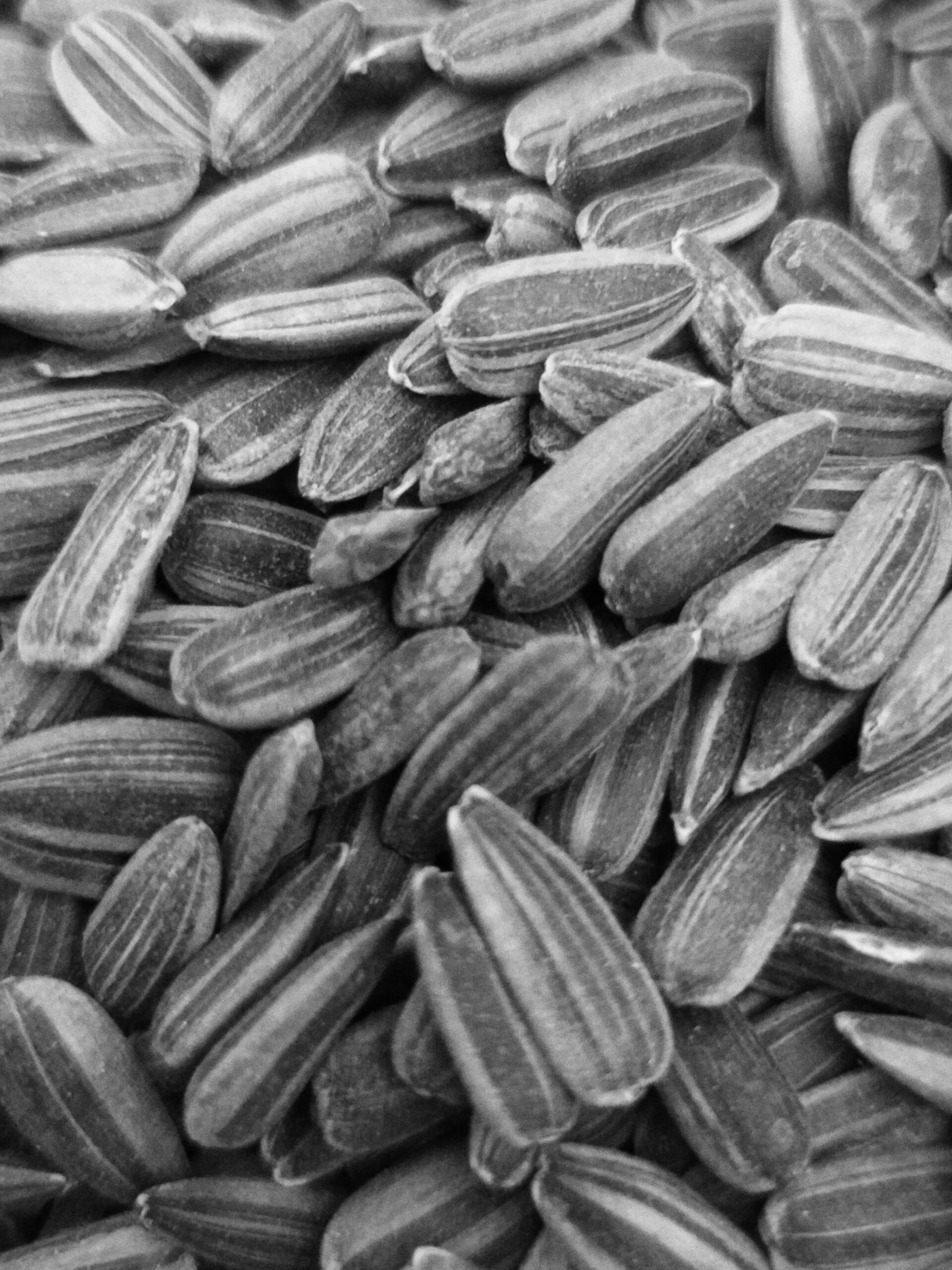


SEEDS
Seeds: Contained in the center of the flower; high in oil and nutrition.
- Sunflower seeds : Sunflower seeds may help lower blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar as they contain vitamin E, magnesium, protein, linoleic fatty acids and several plant compounds. Furthermore, studies link sunflower seeds to multiple other health benefits.
- Sunflower seeds oil : It’s used as a source of polyunsaturated fat in the diet. People use sunflower oil for high cholesterol and preventing heart disease. It is also used for high blood pressure, eczema, dry mouth, dry skin, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
…………………………………………………………………….
Growth & Cultivation :

- Soil: Prefers well-drained soil, rich in nutrients.Environmental Benefits: Sunflowers are known for their phytoremediation properties: they can help clean up soil contaminated with hazardous substances, like heavy metals or radiation. They can absorb these contaminants through their roots and help in cleaning and restoring the soil.
- Sunlight: Needs full sun (at least 6–8 hours a day).
- Water: Moderate watering; too much water can lead to root rot.
- Season: Typically planted in spring and harvested in late summer or early fall.
………………………………………………………………
Uses :
- Agriculture:
- Sunflower oil: Extracted from seeds; used in cooking and cosmetics.
- Livestock feed: Seeds and by-products are used as animal feed.
- Food:
- Seeds eaten raw, roasted, or used in baked goods.
- Ornamental: Popular in gardens and floral arrangements.
- Environmental: Used in phytoremediation to remove toxins from soil (e.g., heavy metals).
Fun Facts :😯
- The tallest sunflower recorded was over 30 feet (9.17 meters) tall!
- Van Gogh famously painted a series of sunflower paintings.
- In many cultures, sunflowers symbolize adoration, loyalty, and longevity
…………………………………………………………………….
🪴Growing Sunflowers at Home :
Best Conditions:
- Sunlight: Full sun (6–8+ hours daily).
- Soil: Well-draining, slightly acidic to neutral (pH 6.0–7.5).
- Spacing: 6–12 inches apart for smaller varieties, 1.5–2 feet for tall types.
How to Plant:
- When: Plant seeds after the last frost.
- How deep: Sow seeds 1–1.5 inches deep.
- Watering: Keep soil moist but not soggy until sprouting; then water regularly.
- Support: Tall varieties may need stakes to prevent bending or snapping.
Common Varieties:
- Mammoth: Giant heads, great for seed harvesting.
- Teddy Bear: Dwarf and fluffy, perfect for pots.
- Autumn Beauty: Multi-colored petals in fall shades.
………………………………………………………
Symbolism of Sunflowers :
Sunflowers have powerful symbolic meanings across cultures:
| Symbolism | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Adoration & Loyalty | Due to their sun-facing nature. |
| Happiness & Positivity | Bright color and bold blooms. |
| Longevity | Long-lasting flowers and durable seeds. |
| Spiritual Connection | In some traditions, they represent faith or divine light. |
| Good Fortune | In Chinese culture, they symbolize vitality and good luck. |
Industrial & Commercial Uses :
Agriculture & Food:
- Sunflower Oil: Popular cooking oil that’s heart-healthy and high in Vitamin E.
- Birdseed: A major component of commercial bird food.
- Snack Foods: Roasted sunflower seeds are common snacks.
Industrial:
- Biofuel: Sunflower oil is used in biodiesel production.
- Cosmetics: Found in lotions, conditioners, and skincare products.
Environmental:
- Phytoremediation: Used to clean contaminated soil (e.g., Chernobyl, Fukushima).
- Pollinator Plant: Attracts bees and butterflies, supporting biodiversity.
if here you found any mistake please inform me. Thanks for your valuable time 💖